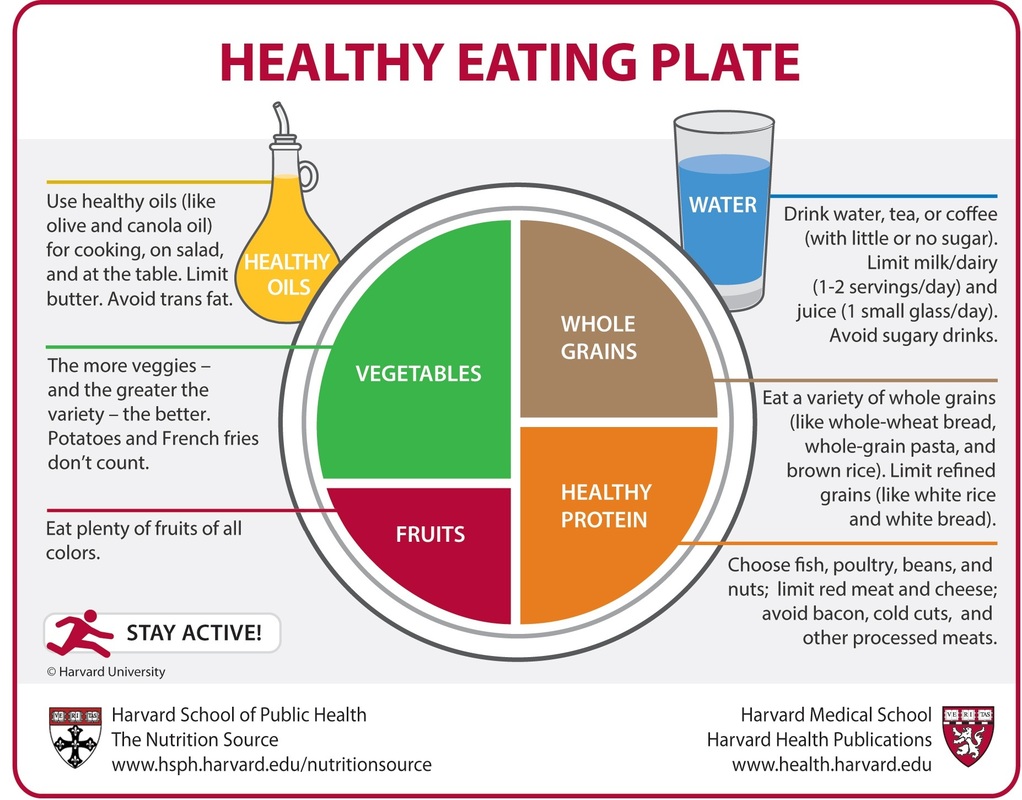
Please visit Nutrition.gov. and https://www.myplate.gov/
Nutrition Vocabulary
Body Mass Index - A measure of body fat estimated from a person's height and weight. A healthy BMI is defined as 18.5 to 24.9. BMI = weight (in kilograms) divided by height (in meters) squared. Using English units, multiply weight in pounds by 703, then divide the result by height in inches, and divide that result by height in inches.
Carbohydrate - The sugars and starches in food that provide the body with most of its fuel. Carbohydrates are one of three primary nutrients along with fats and proteins.
Calorie - The unit for measuring the amount of energy in food.
Carcinogen - Any substance that can cause cancer.
Carcinogenesis - The process by which a normal cell becomes cancerous.
Cholesterol - A waxy, fat-like substance produced by the liver and found in all food from animal sources; an essential component of body cells and a precursor of bile acids and some hormones.
Fat - One of the three major nutrients, along with carbohydrates and proteins.
Fatty Acids - Components of fats that can be used for energy by cells.
Fiber - A substance found in plant foods that the body can't digest.
Fructose - A simple sugar found in corn syrup, honey, and many sweet fruits.
Genetically Modified Organism, or GMO - is an organism that has had its DNA altered or modified in some way through genetic engineering. In most cases, GMOs have been altered with DNA from another organism, be it a bacterium, plant, virus or animal; these organisms are sometimes referred to as "transgenic" organisms.
High-Density Lipoprotein - So-called good cholesterol. This lipoprotein (a substance made of fat and protein) removes cholesterol from arteries.
Lipids - Fats, oils, and waxes that serve as building blocks for cells or as energy sources. Lipids are also capable of accumulating in the artery walls to form plaque.
Low-Density Lipoprotein - So-called bad cholesterol. If there is too much LDL in the blood, it can collect on artery walls, narrowing them and making heart attacks and strokes more likely.
Macronutrients - Substances that provide energy and that the body needs for growth. The main categories are: fat, carbohydrate, and protein.
Micronutrients - Vitamins and minerals needed to maintain normal body functions and prevent certain illnesses.
Monosodium Glutamate - is the sodium salt of glutamic acid, one of the most abundant naturally occurring non-essential amino acids. Monosodium glutamate is found naturally in tomatoes, cheese and other foods.
Nutrients - Substances in foods that the body needs to survive.
Obesity - A body weight that is much higher than is healthy. Defined as having a body mass index of 30 or more. Obesity puts a person at greater risk of developing numerous chronic diseases.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids - Beneficial fats, also known as n-3 fatty acids. These are polyunsaturated fat found in fatty fish, such as salmon.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids - Fatty acids found in certain foods that the body needs for good health but can't make on its own. Also known as n-6 fatty acids.
Overweight - A body weight above the healthy range but not obese. Usually defined as a body mass index of 25 to 29.9.
Polyunsaturated Fat - A type of fat that is abundant in soybean, corn, cottonseed, safflower, and sunflower oils, as well as in fatty fish. One type, omega-3 fats, are especially important for cardiovascular health.
Probiotic - Live microorganisms used to benefit health, such as the L. acidophilus bacteria found in yogurt.
Protein - One of the three major nutrients (along with carbohydrates and fats). It is used by the body for building and repairing tissues. Protein is derived primarily from animal sources but can be obtained from nuts and seed, some grains, and other plant sources.
Saturated Fat - A type of fat found in animal foods such as meat, poultry skin, butter, and whole-milk dairy products, as well in as palm and coconut oils. A diet high in saturated fat tends to raise blood levels of unhealthy low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
Triglyceride - The primary type of fat in the body and in the diet, formed from three fatty-acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. This fat can raise the risk for heart disease when elevated.
Trans Fatty Acid - A type of fat made during hydrogenation of liquid vegetable oil. Trans fats are found in many solid margarines, commercially prepared baked goods, and fried foods in many restaurants. Trans fats increase harmful low-density lipoprotein, decrease protective high-density lipoprotein, and promote blood clotting and inflammation. Also known as trans fat.
Carbohydrate - The sugars and starches in food that provide the body with most of its fuel. Carbohydrates are one of three primary nutrients along with fats and proteins.
Calorie - The unit for measuring the amount of energy in food.
Carcinogen - Any substance that can cause cancer.
Carcinogenesis - The process by which a normal cell becomes cancerous.
Cholesterol - A waxy, fat-like substance produced by the liver and found in all food from animal sources; an essential component of body cells and a precursor of bile acids and some hormones.
Fat - One of the three major nutrients, along with carbohydrates and proteins.
Fatty Acids - Components of fats that can be used for energy by cells.
Fiber - A substance found in plant foods that the body can't digest.
Fructose - A simple sugar found in corn syrup, honey, and many sweet fruits.
Genetically Modified Organism, or GMO - is an organism that has had its DNA altered or modified in some way through genetic engineering. In most cases, GMOs have been altered with DNA from another organism, be it a bacterium, plant, virus or animal; these organisms are sometimes referred to as "transgenic" organisms.
High-Density Lipoprotein - So-called good cholesterol. This lipoprotein (a substance made of fat and protein) removes cholesterol from arteries.
Lipids - Fats, oils, and waxes that serve as building blocks for cells or as energy sources. Lipids are also capable of accumulating in the artery walls to form plaque.
Low-Density Lipoprotein - So-called bad cholesterol. If there is too much LDL in the blood, it can collect on artery walls, narrowing them and making heart attacks and strokes more likely.
Macronutrients - Substances that provide energy and that the body needs for growth. The main categories are: fat, carbohydrate, and protein.
Micronutrients - Vitamins and minerals needed to maintain normal body functions and prevent certain illnesses.
Monosodium Glutamate - is the sodium salt of glutamic acid, one of the most abundant naturally occurring non-essential amino acids. Monosodium glutamate is found naturally in tomatoes, cheese and other foods.
Nutrients - Substances in foods that the body needs to survive.
Obesity - A body weight that is much higher than is healthy. Defined as having a body mass index of 30 or more. Obesity puts a person at greater risk of developing numerous chronic diseases.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids - Beneficial fats, also known as n-3 fatty acids. These are polyunsaturated fat found in fatty fish, such as salmon.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids - Fatty acids found in certain foods that the body needs for good health but can't make on its own. Also known as n-6 fatty acids.
Overweight - A body weight above the healthy range but not obese. Usually defined as a body mass index of 25 to 29.9.
Polyunsaturated Fat - A type of fat that is abundant in soybean, corn, cottonseed, safflower, and sunflower oils, as well as in fatty fish. One type, omega-3 fats, are especially important for cardiovascular health.
Probiotic - Live microorganisms used to benefit health, such as the L. acidophilus bacteria found in yogurt.
Protein - One of the three major nutrients (along with carbohydrates and fats). It is used by the body for building and repairing tissues. Protein is derived primarily from animal sources but can be obtained from nuts and seed, some grains, and other plant sources.
Saturated Fat - A type of fat found in animal foods such as meat, poultry skin, butter, and whole-milk dairy products, as well in as palm and coconut oils. A diet high in saturated fat tends to raise blood levels of unhealthy low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
Triglyceride - The primary type of fat in the body and in the diet, formed from three fatty-acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. This fat can raise the risk for heart disease when elevated.
Trans Fatty Acid - A type of fat made during hydrogenation of liquid vegetable oil. Trans fats are found in many solid margarines, commercially prepared baked goods, and fried foods in many restaurants. Trans fats increase harmful low-density lipoprotein, decrease protective high-density lipoprotein, and promote blood clotting and inflammation. Also known as trans fat.